Once hailed as a triumph of public health, water fluoridation is now under intense attack in the US.
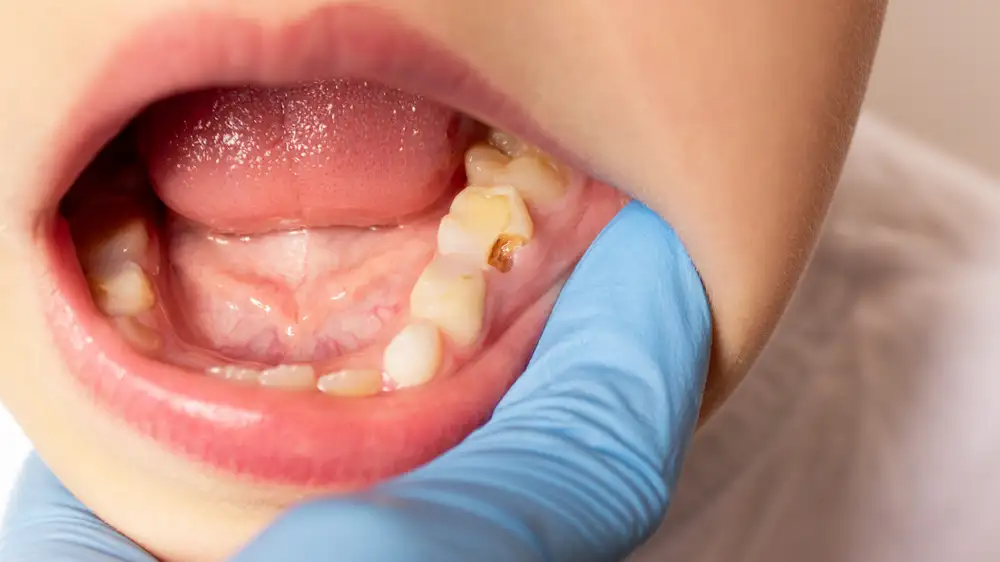
Despite decades of data proving its efficacy at protecting teeth from decay—particularly children's teeth—two states have now banned the use of fluoride in public water, and communities around the country have followed suit or are considering doing the same. The current US health secretary, Robert F. Kennedy Jr., who is known for his anti-vaccine advocacy and for peddling conspiracy theories, has pledged to remove fluoride from US water.
Now, a pair of researchers at Harvard—Sung Eun Choi and Lisa Simon—have modeled exactly what will happen in the US if Kennedy follows through on his pledge: The number of cavities and decayed teeth in American children and teens (ages 0–19) will increase by an estimated 7.5 percentage points over the first five years. That means there will be 25.4 million more rotten teeth in the mouths of children and teenagers. The dental bills for the added decay will total at least $9.8 billion in that time. Other costs, such as loss of work among parents, were not included, making the financial estimate conservative. But children will also be more miserable, with an estimated loss of 2.9 million quality-adjusted life years.
After 10 years, the number of additional decayed teeth would be 53.8 million at a cost of $19.4 billion.
The analysis, published Friday in JAMA Health Forum, drew from real-world dental utilization and oral health data from a national health survey. It also modeled tooth decay as a function of age, sex, race, ethnicity, and income. The model was calibrated against real dental decay prevalence. Costs for dental work were based on standard rates from the American Dental Association, insurance claims, and prior analyses.
In all, the increased decay and boosted dental costs would disproportionately affect children who are in low-income families, in rural areas, and/or on public health insurance.
The study's findings are likely unsurprising to those in the public health community, who have consistently supported fluoridation. The practice, however beneficial, has a long history of being under attack. After its introduction in the US in 1945, conspiracy theorists claimed fluoridation was a communist plot and a form of government mind control. More recently, critics have claimed that fluoridation lowers IQ.
The data linking water fluoridation to low IQ is controversial. Many of the studies on the topic are of poor quality and have numerous confounding factors and flawed methods. Many compare IQ levels in communities in China and other countries, where there are areas with water that is naturally high in fluoride—much, much higher than what is intentionally added to US water. Further, a federal meta-analysis—a type of study that aggregates and reanalyzes data from independent studies—has been plagued by criticism for bias, poor statistical methods, and a lack of data transparency.
But despite the controversy, one thing is clear in all the data and debate: Any possible association with low IQ and fluoridation only occurs at excessive levels—levels more than twice the amount used in the US and recommended by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The CDC recommendation for water fluoridation levels is 0.7 mg/L, while potential harms are not observed until water levels exceed 1.5 mg/L. Some areas in China have natural levels as high as 11.8 mg/L.
The authors of the new study conclude that, at current US levels, the benefits are clear.
"These findings suggest that, despite the potential harms of excessive fluoride exposure, fluoridation at safe levels offers both individual and societal benefits that would be at risk."
 Study Finds Weed Use Linked To Early Heart Disease
Study Finds Weed Use Linked To Early Heart Disease